The Impact Of Global Headwinds And Tailwinds On Southeast Asia’s Venture And Tech Ecosystem

A bull run for venture capital funding in 2021
Global technology startup funding clocked in at a record $621 billion in 2021. Southeast Asia startups raised almost $25 billion marking its coming of age as an important, albeit young, tech corridor. In the first quarter of 2022, as macroeconomic and geopolitical conditions continue to evolve in a melting pot of spiralling energy costs, inflation, and interest rates coupled with a war in Europe, how will the rest of the year play out?
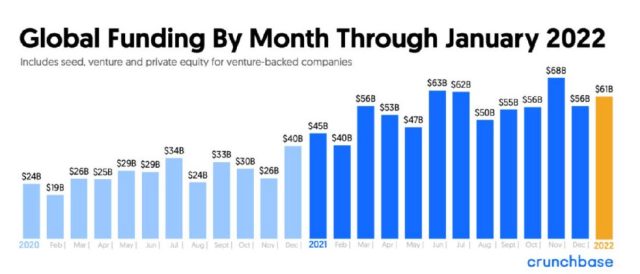
Data from Crunchbase seems to indicate continued strength as global startups raked in $61 billion, the 4th month above the $60 billion mark in the last 12 months. Close to $3 billion was invested globally at seed stage. Startup investors deployed another $18 billion at the early stage and just over $40 billion at the later stage and technology-growth stage. This is amidst a changing landscape where global VC funds are raising record mega funds. Andreessen Horowitz closed on a host of new funds this year, with its eighth fund at $2.5 billion, its fourth bio-related at $1.5 billion, and a third growth fund at $5 billion. Fintech specialist Ribbit Capital closed its seventh fund at just under $1.2 billion, marking its first billion-dollar fund.
While the figures for Q1 2022 Southeast Asia funding are yet to be released, funding news throughout the first three months of the year seems to suggest a good quarter for the region, especially with regard to smaller deal sizes of below $50 million.
Sequoia-backed Multiplier, a startup that enables companies to hire and pay remote workers while complying with local laws, raised $60 million at a $400 million Series B valuation with New York-based Growth Equity Tiger Global as its lead. This came barely 3 months after the company’s Series A of $13.2 million. Tiger Global, together with Cathay Innovation and Sequoia, wrote a cheque to Singapore-based AI Rudder, the leading voice artificial intelligence start-up, leading the $50 million Series B funding – less than 6 months after the company wrapped up its US$10 million Series A in November 2021. Tonik Digital Bank targeting Philippines unbanked consumers closed a $131 million round of Series B equity funding in February 2022 led by Japan’s Mizuho Bank. A VC syndicate led by Vertex and includes Prosus Ventures, AC Ventures, and East Ventures injected $30 million in Series A funding into Indonesia-based fishery and marine platform Aruna. Who would have imagined a Southeast Asia Series A round ballooning to $30 million 12 to 24 months ago!
In parallel, investors have raised concerns about the rapid pace of deals and high valuations. Having said that, it could take time for a correction to reveal itself on a market-wide scale. VC and private equity firms are sitting on immense piles of cash earmarked for startups, and competition for deals remains high. The deal-making pace of Q2 2022 will dictate the direction of venture funding for the rest of the year.
Geopolitical risk threatens to trip up venture capital’s global stride
The venture capital model is predicated upon fast growth and rapid scaling. Adding to the lingering pandemic woes is a crucible of geopolitical risk involving the world’s largest nations US, China, and Russia. For VCs, these geopolitical risks can make it more difficult to raise capital from LPs from sanctioned countries. Increased and enhanced due diligence will be necessary to avoid raising capital from sanctioned sources. Speaking to entrepreneurs in Singapore, Indonesia, and Malaysia, we observe that Southeast Asia startups have little to no dealings with Russian investors. However, some startups we spoke to have reported various delays in their supply chains, especially for parts that originate from Europe.
A Reuters report in March 2022 highlighted that global investors have pursued a re-allocation strategy into crypto and blockchain and away from real estate and bond funds, seeking exposure to a sector they believe could withstand the fallout from the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Venture capitalists invested around $4 billion in the crypto space in the last three weeks of February 2022. Bain Capital Ventures, a unit of private equity firm Bain Capital, for instance, announced in March 2022 that it is launching a $560 million fund focused exclusively on crypto-related investment.
Rising Inflation, Rising Interest Rates: A Threat To Venture Capital And Entrepreneurship?
For the first time since 2018, the Federal Reserve lifted the target for its federal funds rate by a quarter of a point, in order to battle rising inflation, thus signalling the end of a long-lasting pool of cheap capital for companies. Based on historical rate hikes globally, interest rates when they do change are expected to do so gradually. Three or four rate increases by the end of this year could add up to 1% or more to base interest rates in the US.
While higher interest rates will likely lead to a pullback in liquidity, this might have a balancing effect in that it may prevent market pricing and valuations from being driven up to unsustainable levels over the next few years.
The reduction in liquidity may also push VCs and founders to seek alternative forms of capital financing, including venture debt, which will in turn come at higher borrowing costs with venture lenders mirroring (or at least partly mirroring) any interest rate increases in the market at large.
There are two types of companies that need to be careful: companies that are “all tech and no revenue” or “all revenue and no tech”. The critical question is whether these companies are indeed solving real problems for people in a sustainable manner.
Further, such a liquidity pullback may have a disproportionate impact on later-stage technology companies that are pre-IPO (as we witnessed in Q1 2022 in the US). In this scenario, founders and investors will likely delay major liquidity events in order to prevent valuation discounts, given the recent poor performance of many newly listed technology companies.
It’s not all doom and gloom, however. Many technology companies that had a funding event in the past 12 months have likely raised more cash than needed. These companies will likely have to cut expenditures with the aim of extending their cash runways.
Companies can also raise extension rounds, offering shares at the same price as the most recent funding round. Extension rounds were common at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic as they allowed investors to double down on promising companies without having to face steep valuation uplifts amidst an uncertain trading environment.
Many companies with healthy cash flow turn to venture debt and growth debt to shore up balance sheets. A prime example in 2020 was AirBnB which turned away from equity in favour of $2 billion debt at a 10% interest rate from Silver Lake, shoring up its balance sheet despite having close to $4 billion in cash reserves already.
And not to forget that such moments can offer a silver lining for strong founders; market share can be hard to grow when times are good and competition fierce, and perhaps more easily gained during a downturn provided the company is well-financed with a strong team in place.
John Chambers, Chairman Emeritus of Cisco and founder and CEO of Palo Alto’s JC2 Ventures, shared his views that startups are nimble and flexible which works in their favour, highlighting examples of how Cisco and Amazon had trod on similar paths to becoming industry leaders.
Tight Labour Market
It is likely that the Southeast Asian tech ecosystem is entering a golden phase as the tech market continues to grow strongly over the years, speedbumps notwithstanding. Global and pan-Asian tech giants have recognised the region as a strong potential growth engine as part of their global ambitions. As these giants expand in Southeast Asia, the competition to attract and retain talent is becoming a challenge among startups and their larger counterparts. Startups are finding it tough to hire new and replacement employees and expensive to compete with their better-funded, larger, global competitors.
Speaking to regional startup founders and CFOs, we observed a few notable trends. Product, Technology, and Sales are the most challenging positions to fill. There is a growing trend of candidates who accept job offers but do not turn up for work on Day 1. Their reason: they have been offered up to 50% or even 100% more in salary to jump ship. Candidates are also asking for sky-high salaries and are attracted to “frontier” tech like crypto and Metaverse companies.
Startup CFOs tell us that they try to counter these trends with strong and regular internal communications and frequent external initiatives aimed at potential new applicants. Social media, such as LinkedIn, is a valuable tool to grow the employer brand influence of a company. A startup we surveyed is launching what it calls a “Craftsmen Program” to retain team members who have strong coding skills by providing them with visible career path progressions. Last but not least, the delayed nature of the ESOP (employee stock option plan) vesting schedule does also help with retention.
The role of debt financin
2008 (GFC), 2020 (COVID-19) and now 2022. Bumpy years where prudent leadership teams were/are eager to hold on to more cash and shore up balance sheets.
Debt financing can help companies prolong the life of expensive equity already raised. Having an extra 20% or 30% cash cushion gives leadership teams more options by extending the company’s runway, accelerating growth, and staying ahead of the competition.
As for rising interest rates, venture lenders will continue to price in risk and mirror market movements. Where bank rates edge upwards venture lenders are expected to generally mirror that movement by way of interest rate adjustments and even adjustments to warrant option coverage, all with the objective of risk-adjusted pricing. In fact, increased interest rates notwithstanding, our conversations with other regional venture debt operators point to strong deal flow in H1 2022. From Europe to India, and in Southeast Asia considering our own deal flow pipeline, indications are positive that a strong lending pace will continue into the rest of the year. However, lenders are also more cautious of who they lend to and will necessarily tighten the qualification requirements and their credit lens.
