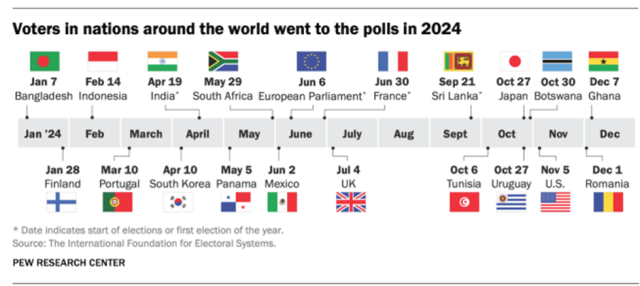
Singapore witnessed a handover of power. Indonesians elected a new President. 2024 saw voters from more than 60 countries go to the polls. The year has been a tumultuous one. The global landscape was marked by political shifts and economic uncertainties, creating a potentially complex backdrop for the tech and venture capital industry.
And after a surge in deals and valuations in 2021 followed by a precipitous decline for most of 2022 with some recoveries in 2023 (mainly driven by AI and sustainability sectors), there were optimistic expectations for a tech and venture capital recovery in 2024. However, 2024 turned out to be a year of recalibration and adjustment for Southeast Asia’s tech and venture scene, marked by a significant decline in funding and a shift in focus towards profitability and sustainability. As we turn the page to 2025, it’s time to assess how the region’s tech landscape has evolved and what trends have emerged.
2024: Revisiting The Year
Profitability Takes Priority: The decline in funding forced startups to prioritize sustainable revenue and profitability over aggressive growth. Traveloka’s turnaround, from a cancelled SPAC IPO to profitability, exemplifies this trend. With the recovery of the travel sector, Traveloka was able to use its internal cash to do an early repayment of its $300 million private credit loan that was due in 2026 to a group of lenders that include BlackRock.
Agritech Struggles: Agriculture is the third largest contributor to Indonesia’s GDP in 2022 at 12.4%, after trade and manufacturing. With a declining farmer population, agritech was seen as a means to improve productivity and towards food security. However, despite the millions invested into tech startups in the agricultural sector, the agritech sector tackling fruits and vegetables to fish and shrimps faced challenges across Indonesia and Vietnam, with several high-profile startups facing alleged financial irregularities.
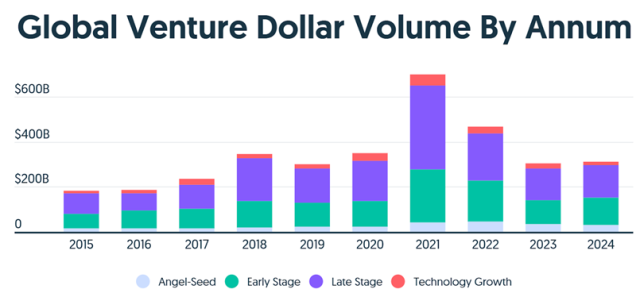
AI Dominates: Globally, AI emerged as the star of the show, attracting close to a third of all global venture funding. One out of every three VC dollars invested globally in 2024 went to an AI startup, reflecting a continued coalescence around the vertical that some investors fear is having a distorting effect on the market. Funding for AI and ML startups accounted for 35.7% of all VC global deal value last year, according to PitchBook data. In North America, the vertical grabbed nearly half of all VC dollars. Globally, investment in AI and ML startups increased more than 50% to $131.5 billion (Source: PitchBook).
2025: Recovery Takes Root
While 2024 was a challenging year, there is increased optimism for 2025, with modest signs of recovery and renewed optimism in Southeast Asia’s tech and venture scene.
Modest Funding Rebound: Global venture funding in 2024 saw a marginal increase compared to 2023, with AI driving the most significant year-over-year growth. Total startup funding in 2024 reached approximately $314 billion, up from $304 billion in 2023, according to an analysis of Crunchbase data. Despite this slight uptick, both late-stage and seed investments faced sharp declines. Late-stage funding plummeted by 76.9%, while seed-stage investments dropped by 52.4%, underscoring ongoing challenges in the broader funding landscape.
Regional Government Backing for Tech: Governments across Southeast Asia are ramping up support for the tech sector through initiatives like tax incentives, grants, and funding programs. In October 2024, Malaysia’s sovereign wealth fund, Khazanah Nasional Berhad, launched Jelawang Capital Sdn Bhd, a national fund-of-funds aimed at nurturing local fund managers and attracting regional players with expertise and capital. Similarly, Indonesia unveiled its Danantara Indonesia Sovereign Fund, boasting an initial asset base of approximately US$600 billion (Rp9,429.8 trillion), designed to invest both domestically and internationally.
DeepTech, DefenceTech, and AI Take Center Stage: Artificial intelligence remains a key driver of innovation and investment, with startups leveraging AI and deep tech capturing significant investor interest. This has been further bolstered by President Trump’s ambitious $500 billion Project Stargate with a focus solely on AI. Sustainability and impact are also gaining traction, as both investors and startups prioritize solutions addressing environmental and social challenges. Meanwhile, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the rise of healthtech and medtech startups, which are developing innovative solutions to improve healthcare access and affordability. Additionally, global conflicts have spurred the emergence of DefenceTech as a prominent sector, drawing keen interest from venture capitalists. For instance, Shield AI, a defense tech company, is building Hivemind — an AI pilot designed to enable swarms of drones and aircraft to operate autonomously without GPS, communications, or human pilots. The company recently secured a $200 million funding round from notable investors, including Palantir, Airbus, and L3Harris, as reported by the Financial Times.
Another trend reshaping the biopharma landscape is the rising influence of Chinese innovation. In 2024, Chinese biotechs accounted for one-third of global pharma licensing deals — a remarkable leap from nearly zero a decade ago. This surge reflects the growing recognition of high-quality science emerging from China, as well as the cost advantages these innovations offer. While the United States remains the epicentre of biopharma innovation, the industry is increasingly embracing a collaborative global ecosystem where groundbreaking science can transcend geographic boundaries to thrive.
CES 2025: Innovations Galore
CES 2025 has once again highlighted the forefront of technological advancements, showcasing how AI is becoming an essential part of both business and everyday life. This transition from viewing AI as merely a tool to recognizing it as a fundamental component of business operations is a significant milestone. Companies are now integrating AI into various areas such as coding, community building, sales, risk management, and even legal and operational processes, unlocking limitless possibilities. This evolution not only boosts efficiency and productivity but also paves the way for new opportunities in innovation and problem-solving. The potential impact of these advancements on our future and our interaction with technology is truly exciting and beyond anything we had previously imagined.

Humanoid robots like Unitree’s G1 and Realbotix’s Aria are truly impressive with their advanced motor technology and fluid movements. These robots are capable of expressing emotions, engaging in conversations, and performing human-like abilities such as walking and jumping. They are already being used in various fields, including hospitality, education, and healthcare. The Unitree G1 humanoid robot, approximately 127 cm tall and weighing 35 kg, is capable of a wide range of movements, thanks to its 23 to 43 joint motors (depending on the specific G1 model). The high mobility of the G1’s joints enables it to perform several everyday human actions, such as moving from standing to squatting positions, turning its body, and waving.
Conversely, Realbotix’s Aria showcases advanced motor technology for fluid movements and a modular design, making her suitable for various applications, including personal companionship and travel convenience. In healthcare, humanoid robots are being explored for roles such as patient care assistants, helping with tasks like taking vitals, administering medication, and providing emotional support. They are also being considered for elderly care, offering companionship and assistance with daily activities.
NVIDIA’s CEO Jensen Huang, unveiled a transformative vision for the future of artificial intelligence, emphasizing the emergence of Agentic AI — a new class of digital workers capable of autonomously understanding complex tasks, formulating plans, and executing actions with minimal human intervention. This groundbreaking development holds significant implications for industries worldwide, as it paves the way for advanced automation systems that can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain precision at scale. By enabling machines to operate with greater autonomy and intelligence, businesses stand to unlock unprecedented levels of productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage in an increasingly digital-first economy. Huang’s insights underscore NVIDIA’s commitment to driving the next wave of AI innovation, positioning the company at the forefront of this technological revolution.

Can a spoon truly alter the taste of food? Remarkably, the answer is yes. Japan’s Kirin showcased an ingenious electronic spoon that utilizes mild electrical stimulation to enhance the salty and umami taste of low-sodium foods — without the need for additional sodium. This breakthrough technology addresses pressing global health challenges associated with excessive salt consumption, offering a novel solution to improve dietary habits and support better nutrition management. Costing US$126, it is currently only available in Japan.
Finally, you will no longer have to worry about running out of ingredients in your fridge. Samsung partnered Instacart to make grocery shopping more convenient by allowing consumers in the United States to order groceries directly from their Samsung Bespoke refrigerator screens. Using Samsung’s AI Vision Inside technology and Instacart’s product-matching API, users can manage their food inventory and replenish items with ease.
These insights from JPMHC 2025 and CES 2025 underscore how technology is revolutionizing different industries in profound ways. At these events, several key innovations showed just how pivotal tech advancements are in shaping the future. AI has a growing role across multiple domains, from smart home devices to enterprise solutions. AI is becoming indispensable in automating tasks, analyzing vast amounts of data, and enabling predictive analytics. Businesses are leveraging AI to enhance operations, improve customer service, and drive innovation. Overall, the insights from these conferences highlight how technology is not just an accessory but a driving force reshaping industries and enhancing our quality of life.